What is pH?
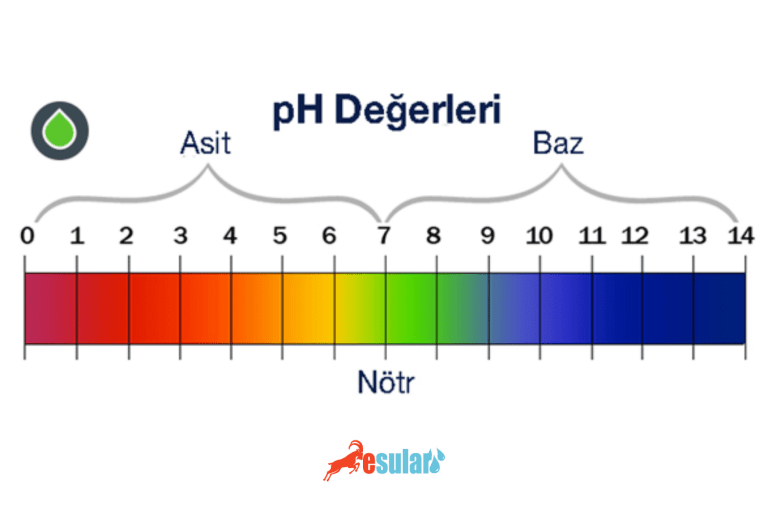
The measure used to understand the acid or alkali values of a substance is called pH (potential hydrogen). Measurement is made according to the density of acid-natured hydrogen ions in the substance. The pH scale is between 0 – 14. 0 means extreme acid, 14 means extreme alkali. A pH level of 7 indicates that the substance is neither acid nor alkali, meaning it is neutral.
Soil pH (Soil Reaction)
It expresses whether a soil is acidic, neutral, or alkaline in structure. This value being low or high affects plant growth, plant nutrient availability in the soil, and plant nutrient uptake. While some Plant Nutrients cannot dissolve in water at high pH values, some Plant Nutrients cannot be taken up by roots at low pH values. The pH value required for the optimum development of each plant is different. Generally, the pH requirements of plants vary between 5.5 and 7.0. In agricultural production, it is very important to constantly control these values and perform irrigation and fertilization through these values.
PLANT | pH |
Potato | 5,5-6 |
Tobacco | 5,5-6,5 |
Wheat | 6,5-8,5 |
Tea | 4,5-6 |
Paddy | 5,5-7,5 |
Sunflower | 6,5-7,5 |
Cotton | 6,5-7,5 |
Corn | 6-7 |
Tomato | 3,9-4,3 |
Soil pH is measured by two methods;
- By electrical method (pH meter)
- By dye methods (Indicators)
Factors affecting the change of soil reaction;
- CO2 gas (increases acidity),
- Organic matter content,
- Leaching of bases,
- Fertilizer content (ammonium sulfate, sodium, nitrate, calcium cyanamide etc.),
- Plants- microorganisms,
- Seasons and
- Soil texture.
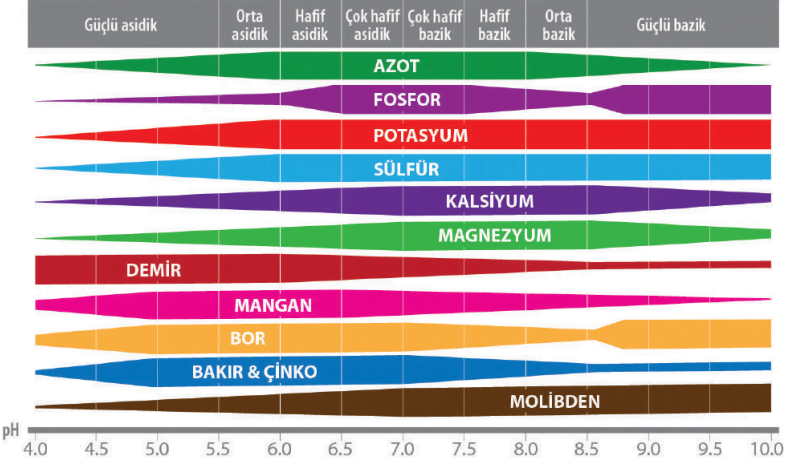
Effect of alkaline and acidic soil conditions on the availability of some nutrients;
Nutrient
Alkaline soil conditions (High soil pH)
Acidic soil conditions (Low soil pH)
Nitrogen
Especially in surface applications in the form of urea, the available amount decreases.
Since nitrification decreases, the amount of nitrogen mineralized from organic substances decreases.
Phosphorus
Its availability decreases in soils with high pH.
In acid conditions, its uptake decreases due to poorly soluble iron and aluminum phosphate.
Potassium, Magnesium
In high pH soils, its availability decreases due to the antagonistic effect of calcium present at high levels.
The available amounts decrease due to leaching.
Iron,
Zinc, Manganese, Copper, Boron
Since they form poorly soluble compounds, their uptake decreases. It appears as a microelement deficiency symptom in calcareous soils.
The solubility of Iron and Manganese increases, and the increase in the solubility of these elements along with Molybdenum can have a toxic effect on plants. Likewise, it can also negatively affect the uptake of other nutrients.
Molybdenum
It turns into an unavailable form for plants.
What Happens if Acidity Increases in Soil?
Acidification increases in the soil due to human factors such as chemicals released into the atmosphere and left in water resources from urbanization, industrialization, mining, and construction sectors, unconscious use of chemical fertilizers in agriculture, damage to soil vegetation, and destruction of forests. No matter how much low-pH soils are fed with fertilizers, the plant cannot take up these nutrients. As fertilization is performed to increase the soil's nutritiveness, worse results are obtained.
When soil acidity rises, the solubilities of iron, aluminum, and manganese increase. Phosphorus combines with these elements to form insoluble compounds. The effects of bacteria that enable the decomposition of organic substances, produce nitrate, and keep the amount of nitrogen in the atmosphere stable decrease. The drainage and aeration capacity of the soil decreases. The soil absorbs rainwater with difficulty and its processing becomes harder. The decomposition of organic substances (animal manures, stubble and plant residues, etc.) is delayed. In some cases, the applied phosphorus fertilizers accumulate in the soil and the soil surface takes on a color as if diesel had been spilled. Soil texture (sand, silt, clay ratio) and soil organic matter content determine the soil's resistance to acidification. Light sandy soils, poor in terms of organic matter, are the most fragile soils against acidification.
Reclamation of soils with low pH values
- To raise soil pH, nitrogenous and phosphorus fertilizers containing calcium or direct lime application should be performed on the soil.
- After adjusting the pH, compost can be added to the area. Although this practice does not provide an immediate effect on the soil's pH, it will help it improve over time and provide nutrients to the plants in the area while keeping the soil's acidity level under control.
- Wood ash can also be used to increase soil pH. If this method is preferred, the use of treated wood or black walnut, which are toxic to other plants, should be avoided.
What Happens if pH Increases in Soil?
Generally, soils in arid regions receiving little rainfall have high pH values. It is a type of soil that contains high amounts of calcium, sodium, and magnesium within the alkaline soil structure. High pH values play an important role in the availability of plant nutrients in the soil by plants, soil fertility, and fertilization programs. There are water retention and storage problems in such soils. They have low infiltration capacity, low permeability, and accordingly low drainage.
The reason why soils with high pH values generally have low yields is that high pH prevents the movement of elements such as phosphorus, iron, manganese, zinc, etc., in the soil. In such soils, yield increase can be achieved again by lowering the pH value. However, the effective correction of such soils depends on the alkalinity structure and level of the soil, the quality and quantity of irrigation water, soil structure, and plant pattern.

Reclamation of soils with high pH values
- Add organic matter: The simplest and most organic way to lower the soil's pH level is to make changes in the soil. Adding organic materials such as mulch, pine needles, sphagnum peat moss, and compost, etc., helps to lower the soil's pH level.
- Use acidifying fertilizer: If the soil's pH level is excessively high, adding sulfur-containing acidifying fertilizers such as aluminum sulfate or ammonium sulfate will lower the pH value.
- After applying these methods, wait a few weeks before testing the soil again. It takes time for organic materials and fertilizers to penetrate the soil and change the pH level. Applying these methods over time ensures more effective results; avoid using too much organic matter or fertilizer at once.
Soil pH uptake ranges of microelements;



Yorumlar