How to Grow Alfalfa?
Alfalfa cultivation is an agriculturally important practice and is considered an important forage source in animal nutrition. Alfalfa is used especially in animal nutrition due to its high nutritional value and protein content. Alfalfa cultivation is carried out in order to provide a quality and balanced forage source for the nutrition of animals in the livestock sector. Alfalfa cultivation is also quite common in regions where livestock activities are intense in Turkey. Alfalfa is generally grown in the Marmara, Aegean, Central Anatolia, and Black Sea regions in our country. Since the water-holding capacity of alfalfa is high, it is also an effective plant in preventing soil erosion. Due to the advantages of alfalfa in improving the soil and its use as animal feed, it is considered an important agricultural product in Turkey.
What is Alfalfa?
Alfalfa is an herbaceous plant from the legume family, usually with a quadrangular stem. It has characteristic leaves consisting of three leaflets, and its flowers can usually be white or purple in color. Alfalfa is an important forage plant generally grown as animal feed for pastures. Alfalfa used in livestock is known for its high nutritional value and protein content. With these features, it is considered a quality nutritional source for animals.

Soil Preparation in Alfalfa Cultivation
Soil preparation is a very critical process in alfalfa cultivation. To obtain a productive harvest and ensure the healthy development of plants, soil analysis should be performed first. This analysis determines the nutrient content, pH level, and general structure of the soil. According to the data obtained, soil drainage is important because alfalfa prefers well-drained soils. By providing drainage, water accumulation is prevented, thus creating a suitable environment for plant roots. During the soil tillage stage, aerating the soil and cleaning agricultural residues are of great importance. In addition, the fertilization process is important to meet the nutrient needs of the plant, and this should be done according to the results of the soil analysis. Regular weed control in alfalfa areas is also necessary for the healthy development of the plant.
When is Alfalfa Planted?
Alfalfa sowing is carried out in different periods depending on climate conditions and varieties. Generally, the most suitable times for alfalfa sowing are the spring or autumn seasons. In the spring, the months of April-May can be favorable for alfalfa sowing; in this period, the increase in air temperatures and the warming of the soil offer a suitable environment for the healthy growth of the plant. However, regional differences should be taken into account. In temperate climate regions, especially in the Marmara, Aegean, and Mediterranean regions, alfalfa sowing is common in the spring.

How Much Alfalfa is Sown per 1 Decare of Land?
The amount of alfalfa sowing can vary depending on various factors. Factors such as alfalfa type, soil quality, climate conditions, and sowing methods affect this amount. However, in our country, generally in sowings made with a seeder, between 2 to 3 kilograms of alfalfa seed are sown per decare. For broadcast seeding, up to 4 kilograms of alfalfa seed will be sufficient per decare.
How Long Does Alfalfa Take to Grow?
If alfalfa sowing was done in the spring, it becomes ready for cutting approximately 60-65 days later. The second cutting is done approximately 35-45 days later. In alfalfa, seeing approximately 10% flowering indicates that the time for cutting has arrived.
How is Alfalfa Irrigation Done?
Although alfalfa is generally resistant to drought, it needs certain moisture levels to obtain high yields. The moisture rate of the soil should generally not fall below 50%. During the development process, irrigation can be done using surface or sprinkler systems when the soil dries out. The last irrigation usually takes place 3-10 days before harvest. Since alfalfa is a perennial plant with a deep root system, stress caused by too much or too little water negatively affects the growth, development, and quality of the plant. Therefore, irrigation methods such as surface irrigation are a threat to high yield in alfalfa cultivation. To increase the number of cuttings and forage quality in alfalfa, you can keep the moisture amount at an optimum level thanks to our sensors, which allow your irrigation system to be controlled remotely. For more information, you can examine our article https://esular.com/yoncada-akilli-sulama-sistemleri-ile-ot-verimini-artirin.

How is Alfalfa Fertilization Done?
In alfalfa cultivation, if animal manure has not been applied during the soil preparation period, 25 kg/da of DAP fertilizer will be sufficient. In subsequent years, there is no need for nitrogenous fertilization. Only 20-25 kg/da of TSP fertilizer should be applied in the autumn. One of the incorrect practices carried out in alfalfa fields is giving nitrogenous fertilizer (ammonium sulfate, urea) or animal manure to the alfalfa starting from the second year. It is more beneficial if animal manure is given while preparing the seedbed before sowing. Farm manure and nitrogen given after sowing cause an increase in weeds in the field, weakening of the alfalfa, and shortening of its lifespan.
What are the Pests Seen in Alfalfa?
The weevil (Sitona lineatus), which is one of the main enemies of alfalfa, is an important pest commonly seen in the market that negatively affects alfalfa farming. This pest is known for a black head and a distinct white line on its back. The alfalfa weevil has the characteristic of giving one brood per year and can cause significant damage, generally during the larval period at flowering, by eating the growth points, leaves, and flowers of the plant. To examine the diseases seen in alfalfa, you can examine our article https://esular.com/yonca-hastaliklari.
Alfalfa Harvest
The most suitable harvest period for alfalfa is the period when it flowers by 10%. In this period, it is mowed so that at least 5 cm remains on the ground. After cutting, it is turned in the field for 1 or 2 days depending on weather conditions to ensure it dries. Dried hay is generally preserved in the form of bales. Additionally, in order for the plant to be protected from winter, at least 10 cm of height should be left in the last cutting.

How Much Alfalfa is Obtained from 1 Decare?
Alfalfa is a perennial plant and its lifespan is approximately 7 years. It gives the highest yield in the third year, and then the yield gradually decreases. Forage yield varies according to soil fertility, fertilization, irrigation, and care. Generally, an average of 1 – 3 tons of green forage can be obtained per decare from each cutting. Its dry hay equivalent is 300 – 800 kg. When harvested towards the end of the maturation period, a yield increase is provided, but the nutrient content and digestibility of nutrients decrease.
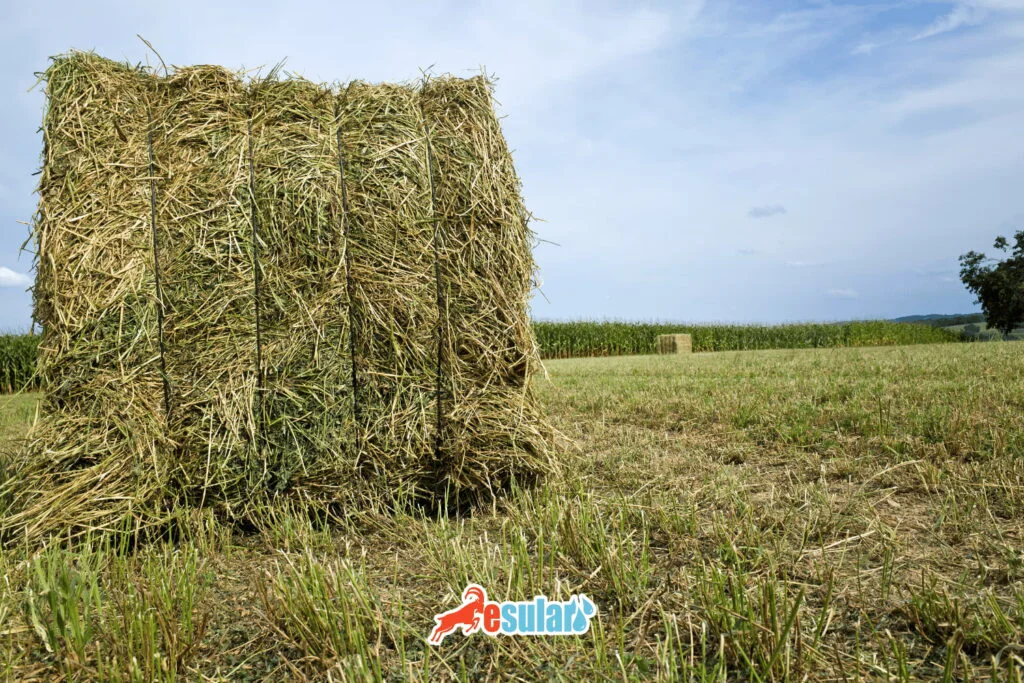

How Many Times is Alfalfa Mowed per Year?
Alfalfa can be harvested 3-4 times a year in most regions, and 7-8 times a year in some regions. The yield amount varies according to the region, climate, and the maturity period in which the alfalfa is harvested.


Yorumlar