How to Cultivate Sainfoin?
Sainfoin cultivation is an activity that stands out in the agricultural sector both for the high nutritional value it provides as a forage crop and its ability to grow even in unproductive soils. Sainfoin (Onobrychis sativa) is a perennial plant from the legume family and is highly resistant to drought and cold thanks to its deep root structure. Except for the first year, hay yield can be obtained from the same field for 5-6 years; when used as animal feed, it meets the nutritional needs of a wide range of livestock, from dairy cattle to small ruminants. While sainfoin supports the development of animals with its protein-rich structure and forage quality, it also contributes to the enrichment of the soil in terms of calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals. Additionally, because it flowers abundantly, it holds an important place in beekeeping activities and is an excellent source of honey for bees. Thanks to its deep roots, it protects and stabilizes soils against erosion, making it an effective plant for erosion control.
What is Sainfoin? Why is it Cultivated?
Sainfoin (Onobrychis sativa) is a perennial forage crop from the legume family, known especially for its ability to be grown in arid and unproductive soils. Except for the first year, the sainfoin plant provides hay yield from the same field for 5-6 years.
Why is it Cultivated?
- Forage Crop: Sainfoin is a plant rich in protein with high forage quality. Thanks to the calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals it contains, it increases the development and yield of animals.
- Soil Improver: By forming nodules on its roots, it has the ability to fix nitrogen into the soil, thereby increasing soil fertility.
- Honey Plant: Because it flowers abundantly, it is an excellent source of honey for bees.
- Erosion Control: Thanks to its deep root structure, it protects and stabilizes soils against erosion.
How is it Used?
- Fresh and Dry Hay: Sainfoin can be fed to animals as fresh or dry hay. Especially when a certain amount is given daily to dairy cattle, digestive system disorders are rarely encountered.
- Silage Making: Sainfoin can also be used as animal feed by making silage.
- Grazing: Since it is resistant to grazing, it is used as a good pasture plant.
- Honey Production: It is valued as a honey-producing plant for bees, which supports beekeeping activities.
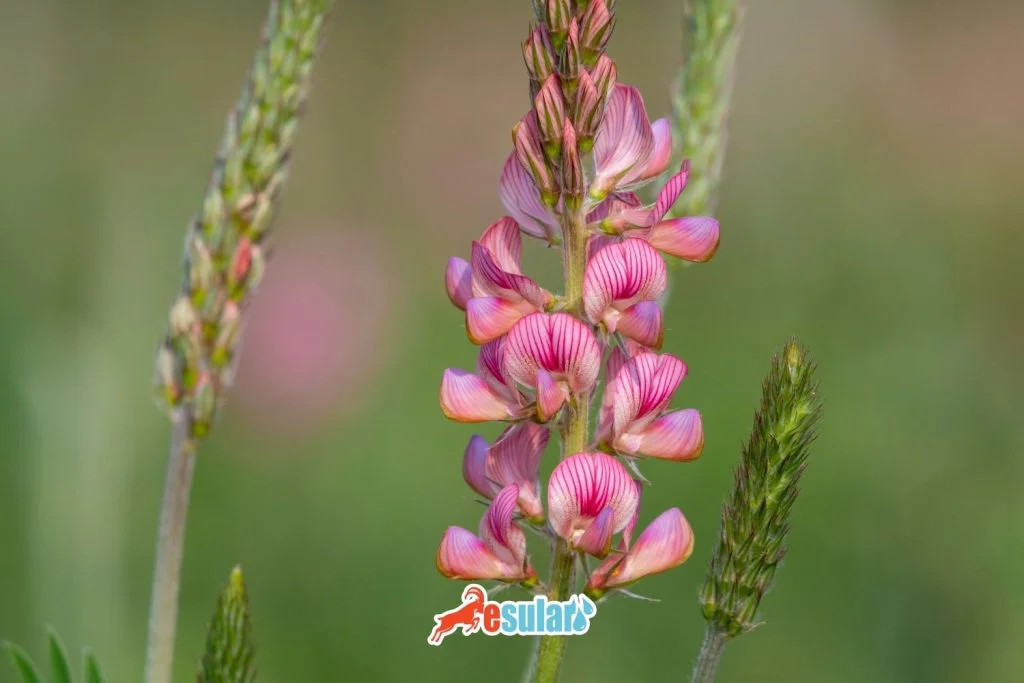

Climate and Soil Structure in Sainfoin Cultivation
The sainfoin (Onobrychis sativa) plant can grow in any climate and is highly resistant to drought and cold. It is only sensitive to cold during the seedling period in the first year it is planted. Its resistance to winter frosts increases as it ages. Thanks to this feature, it can even grow in the Central Anatolia Region under conditions of 300 mm annual rainfall. In places that receive excessive rainfall or are irrigated very frequently, it may catch root and crown rot diseases. Additionally, due to heavy and continuous rains during the flowering period, the plant may not produce seeds. With this adaptation ability, sainfoin can adjust to a wide range of climatic conditions.
In terms of soil requirement, the sainfoin plant is not very selective and can easily grow in soils that are poor in nutrients, arid, and calcareous in structure. However, it shows its best development in deep-structured, permeable, loose, calcareous, and loamy-sandy soils. Although sainfoin is resistant to salinity, it cannot show good development in acidic and water-retaining soils. As the amount of calcium (Ca) in the soil increases, the yield of sainfoin is also positively affected. With its ability to grow especially in dry and calcareous soils, the sainfoin plant contributes to agricultural production by utilizing unproductive lands. For this reason, sowing sainfoin in arid and stony areas allows for the efficient use of such lands. At the same time, it is known for its soil-improving effect. By increasing the amount of nitrogen in the soil, it ensures enrichment in terms of plant nutrients.
Soil Preparation and Sowing in Sainfoin Cultivation
In sainfoin cultivation, a well-prepared seedbed is necessary to achieve successful sowing and high yield. Since sainfoin is a deep-rooted plant, soil preparation begins with deep plowing in the autumn. In the spring, it continues by breaking the clods in the field and pressing the soil. Since the competitive power of the seedlings is low in the sowing year, it is important that the seedbed must be cleared of weeds. This is necessary for the healthy development of the sainfoin. Before sowing, sainfoin seeds must be inoculated with a bacterial culture that fixes the free nitrogen of the air into the soil by forming nodules on their roots. This inoculation process is done using 1 kg of bacterial culture for every 100 kg of seeds. The inoculation process is carried out in a shaded area, and after the seeds are lightly moistened with 10% sugar water, they are inoculated with the bacterial culture. The inoculated seeds should be sown within 24 hours at the latest after being dried in a shaded place.
Since seedlings are damaged by cold in the first year, the most suitable sowing time is the spring months. Sowing should be done with seeders; since sainfoin has large seeds, a cereal seeder can be used. Sowing depth varies between 2.5-7.5 cm depending on the soil type. Under normal conditions, to have 100 plants in a 1 m² area for hay production, 2.8 kg of unhulled seeds should be sown per decare. However, considering that all sown seeds may not germinate for various reasons, approximately 5-6 kg of seeds should be sown per decare. In broadcast sowing, the distance between rows should be between 40-60 cm. In mixed sowings, if a binary mix is made, the row spacing should be 20 cm, and in triple mixes, it should be 20-60 cm. If sowing is to be done with a seeder, the row spacing should be 12.5 cm.
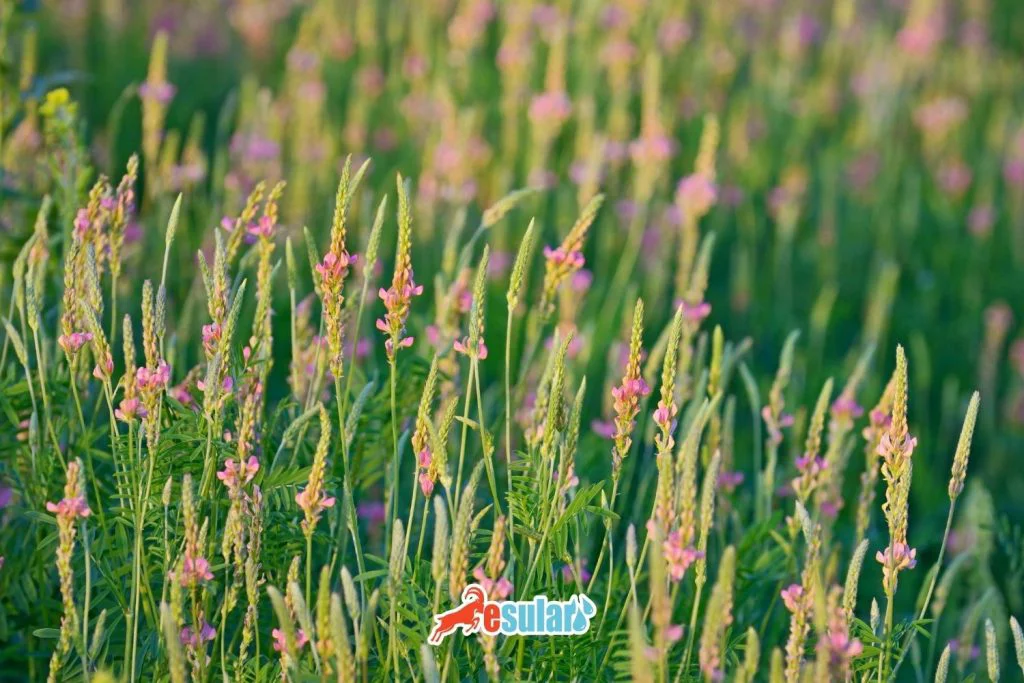

Irrigation in Sainfoin Cultivation
Sainfoin is a forage crop with low water requirements that can be grown in arid and semi-arid regions. To maintain soil moisture during the germination, emergence, and seedling periods after sowing, it is important to irrigate at frequent intervals but in small amounts. Flood irrigation and sprinkler irrigation methods can be used; sprinkler irrigation ensures equal distribution of water. Regular irrigation during the growth period of the plant increases productivity and hay quality. Irrigation performed at the beginning of flowering encourages the second cut and increases annual yield. With irrigation possibilities, the yield of sainfoin can increase by 50-100%.
Fertilization in Sainfoin Cultivation
Fertilization in sainfoin cultivation is important for the healthy development of the plant and for obtaining high yields. Since sainfoin is a plant that fixes nitrogen into the soil, fertilization is generally done only once during sowing. Before sowing, 10 kg of nitrogenous fertilizer (26%) should be applied per decare. During sowing, it is recommended to give 15-20 kg of DAP or TSP fertilizer per decare. Considering that sainfoin develops better in calcareous soils, it should not be forgotten that the yield will increase as the amount of lime in the soil increases. After the initial sowing, it generally does not require additional fertilization because the sainfoin plant has a structure that can meet its own nitrogen needs.

Sainfoin Harvest



Yorumlar