How is Ginger Cultivation Done?
Ginger cultivation is an agricultural activity successfully carried out in regions with suitable climate and soil conditions. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a perennial plant belonging to the Zingiberaceae family, whose roots are used for medicinal and culinary purposes. The ginger plant is widely known as a spice obtained from its roots and used fresh or dried. Ginger is believed to have a number of health benefits. Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, it is used to relieve nausea, improve digestion, and strengthen the immune system. It is also known that ginger provides support to the digestive system, has antioxidant properties, and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Ginger, which is cultivated in many countries, has a wide range of commercial uses. In addition to being used as a spice in the food industry, it is also used in health supplements, cosmetic products, and pharmaceutical products. Therefore, its economic value is also high.
Where Does Ginger Grow?
This root plant naturally grows in regions with hot and humid climates such as India, China, Southeast Asia, the West Indies, and Mexico. These regions have high temperature and humidity levels that provide optimum growth conditions for ginger. In our country, ginger is generally grown in the Mediterranean Region, especially in Antalya and its surroundings. The Mediterranean climate offers a suitable environment to provide the temperature and humidity conditions that ginger needs. However, ginger cultivation can also be done in other tropical and semi-tropical regions when appropriate conditions are provided.
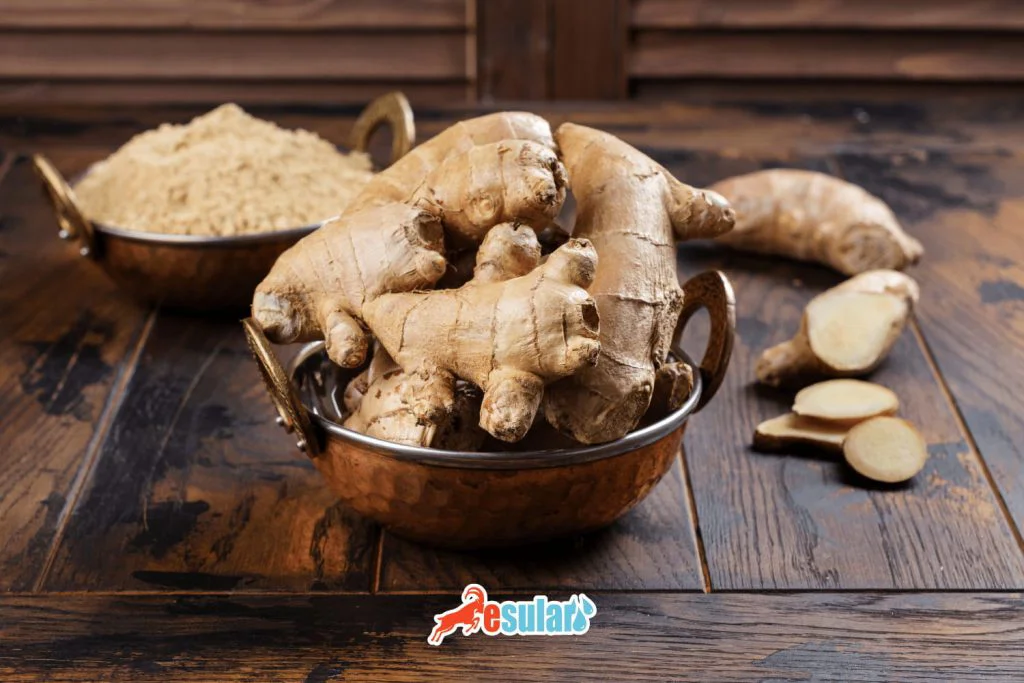

Climate and Soil Structure in Ginger Cultivation
Climate conditions are an important factor in ginger cultivation. Ginger prefers tropical and semi-tropical climates. It generally grows better in hot and humid regions. Ideally, the annual rainfall for ginger cultivation should be between 3000 and 4000 mm. Additionally, it is important that the humidity is high during the plant's sprouting period. The temperature range should generally be between 19 and 28 degrees. Ginger grows best in regions where temperature and humidity are balanced. Soil structure also plays a major role in ginger cultivation. Well-drained, light loamy or clayey loamy soils are ideal for the ginger plant. The soil pH value should be between 6.0 and 6.5; acidic or alkaline soils are not suitable for ginger. Furthermore, it is important to ensure good air circulation in the soil and good drainage of water. Ginger is sensitive to salty soils, so it is important to control the salinity level of the soil.
How to Plant Ginger?
For planting, well-drained, aerated soils with a pH value between 6.0 and 6.5 should be preferred. Ginger rhizomes selected for planting should be approximately 2.5-5 cm long and have at least one or two healthy eyes on them. Rhizomes are prepared by cutting with a sterilized knife. In the field to be planted, rhizomes are planted with a spacing of 20-25 cm between rows and on the row. Each rhizome is planted to a depth of approximately 4-6 cm and covered with a thin layer of soil. Irrigation is performed after planting and kept constantly moist. If seedling cultivation is preferred, healthy ginger rhizomes are selected and waited until they sprout. Then the sprouts are grown in a suitable environment and prepared for planting. After planting, regular irrigation and appropriate fertilization ensure the healthy development of the ginger plant.

Irrigation in Ginger Cultivation
Ginger should receive at least 2000 mm of rainfall distributed annually; irrigation may be required in regions falling below this amount. The first irrigation should be done immediately after planting, and subsequent irrigations should be repeated every 7-10 days depending on the soil type and weather conditions. The amount of irrigation should be adjusted based on the moisture level of the soil and the needs of the plant. Drip or sprinkler irrigation systems support plant development by ensuring more efficient use of water. In the case of growing in pots, the amount of irrigation should be determined before planting, and irrigation should be done when the soil is almost one-third dry. The effective use of irrigation systems ensures the healthy growth of the ginger plant and a productive harvest.
Fertilization in Ginger Cultivation
Before applying fertilizer, a soil sample should be taken and analyzed, and the levels of nutrient elements in the soil should be determined. Fertilizer application is generally done in divided doses during the planting stage and the growth period of the plant. While all of the phosphorus can be applied at the planting stage, nitrogen and potassium should be given in divided doses. Additionally, zinc fertilization can be applied in soils with zinc deficiency. Depending on the needs of the plant, organic fertilizers can be used in addition to macro and micro nutrient elements. Organic fertilizers can increase the plant's nutrient uptake by improving the structural properties of the soil and increase soil fertility. Another important point to consider during fertilizer application is avoiding over-fertilization. Excessive fertilization can negatively affect plant health and harm the environment.
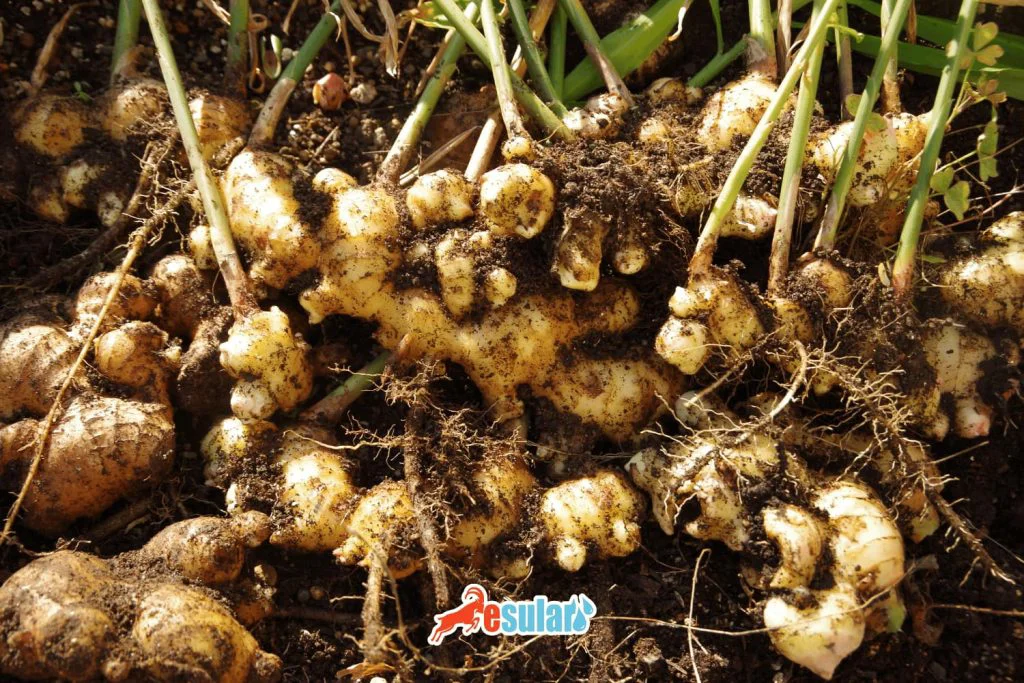

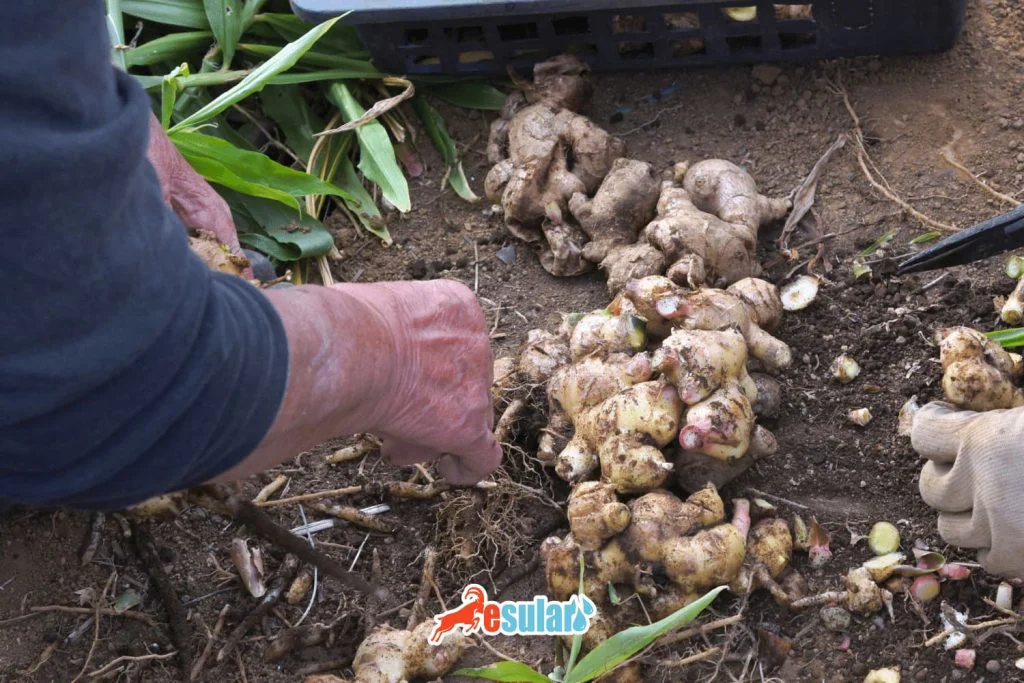
Ginger Harvest
The harvest time of ginger varies according to the purpose of consumption and the way it is used. If ginger is to be used as a dried spice, it must be harvested during the full maturity period. This period may vary depending on growing conditions, climate conditions, and the variety. At full maturity, 50% of the leaves begin to yellow and dry. By stopping irrigation, further maturation of the rhizomes is ensured, and harvest is carried out one month later. In cultivation for vegetable purposes, harvest usually starts after 180 days depending on demand. Important criteria determining the optimum harvest time for fresh ginger include the fiber content, essential oil content, and hardness of the rhizomes. If ginger is to be used for herbal purposes or for the preparation of products such as sugar, soft drinks, pickles, and alcoholic beverages, it can also be harvested approximately 150-180 days after planting. Determining the harvest time correctly is important for the quality and productivity of ginger.
Where is Ginger Used?
Ginger is a versatile plant used in various fields worldwide. Here are some areas of use for ginger:
In the Kitchen: Ginger is a spice frequently used in cooking and dessert making. It is used to add flavor to dishes made with meat, chicken, fish, and vegetables. Additionally, it is used to give aroma and flavor to various desserts, cookies, cakes, and breads.
In Beverages: Ginger is also frequently used in alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages. It can be used in ginger beer, ginger ale, ginger wine, and various cocktails.
For Medicinal Purposes: Ginger has digestive-facilitating, anti-inflammatory, and antiemetic (prevents vomiting) properties. Therefore, it is used in traditional medicine for the treatment of various ailments such as nausea, indigestion, and colds.
As a Health Supplement: Some people use ginger supplements to support digestive health, strengthen the immune system, and reduce inflammation.
In Cosmetic Products: Ginger is believed to have benefits for the skin and is used in some cosmetic products, especially skin care products.
Tea: Ginger tea is a popular beverage known for its health benefits. It is consumed as a natural solution for colds and digestive problems.
Natural Cleaning Products: Ginger oil can be used in some natural cleaning products and deodorants.
Ginger has gained popularity worldwide due to these wide areas of use and health benefits.


Yorumlar