Temperature and Humidity Control in Greenhouses
Temperature and Humidity Control in Greenhouses is quite important for the productivity of greenhouses and the health of plants. Correct temperature and humidity levels provide optimal growth conditions for plants and reduce the risk of disease. Temperature control in greenhouses is generally provided by ventilation systems, heaters, and cooling systems. Humidity control is performed using humidifiers and dehumidifiers. Especially automatic systems monitor temperature and humidity continuously through sensors and make necessary adjustments. In this way, the microclimate needed by the plants is created, providing a healthier and more productive production environment. As Esular, we offer advanced systems for the most suitable temperature and humidity control in your greenhouses. Our high-precision temperature and humidity sensors monitor the climate conditions of your greenhouse instantly and maintain ideal levels with our automatic control systems.
What is the Effect of Temperature and Humidity on Plants?
Humidity:
- Photosynthesis and Transpiration: Humidity is of critical importance for the photosynthesis and transpiration processes of plants. Sufficient humidity ensures that stomata remain open, facilitating carbon dioxide uptake and the expulsion of water vapor.
- Cell Turgor: The turgor pressure of plant cells is maintained with sufficient humidity. This pressure ensures that plants stand upright and maintain their structural integrity.
- Nutrient Uptake: High humidity levels increase the uptake of nutrients from the roots of plants. This supports plant health and growth.
- Diseases and Pests: High humidity can encourage the spread of fungal and bacterial diseases. On the other hand, low humidity levels can prevent the spread of some harmful insects.
Temperature:
- Photosynthesis and Respiration: Temperature directly affects the photosynthesis and respiration rates of plants. While the photosynthesis rate increases within the optimal temperature range, extreme temperatures can cause plants to go under stress and lead to a decrease in the photosynthesis rate.
- Growth and Development: Every plant has an optimal growth temperature range. Temperatures outside this range can slow down or stop plant growth.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Temperature directly affects the flowering and fruiting processes of plants. A specific temperature range ensures that these processes occur healthily.
- Enzyme Activity: Most of the enzymes in plant metabolism show maximum activity within a certain temperature range. Extreme temperatures can negatively affect plant metabolism by disrupting the structure of enzymes.
Humidity and temperature are critical environmental factors that have a direct effect on the health and productivity of plants. Maintaining optimum humidity and temperature levels is necessary for plants to be able to photosynthesize, grow, flower, and stay healthy. For this reason, humidity and temperature control in greenhouses is of vital importance for productive and healthy plant cultivation.
The Role of Climate Control Systems in Humidity Control
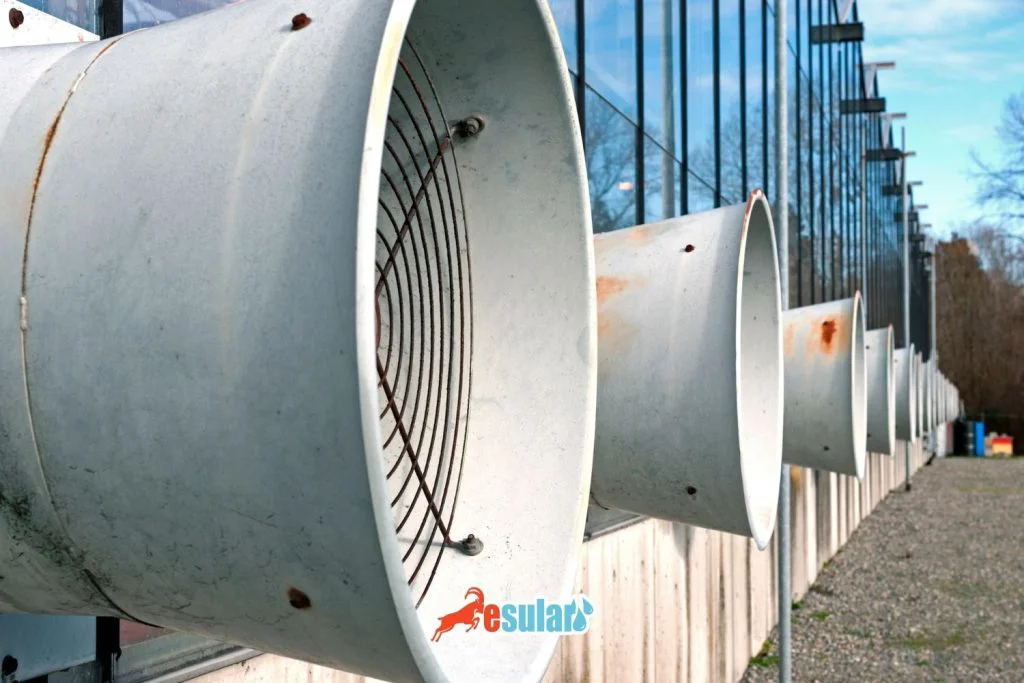
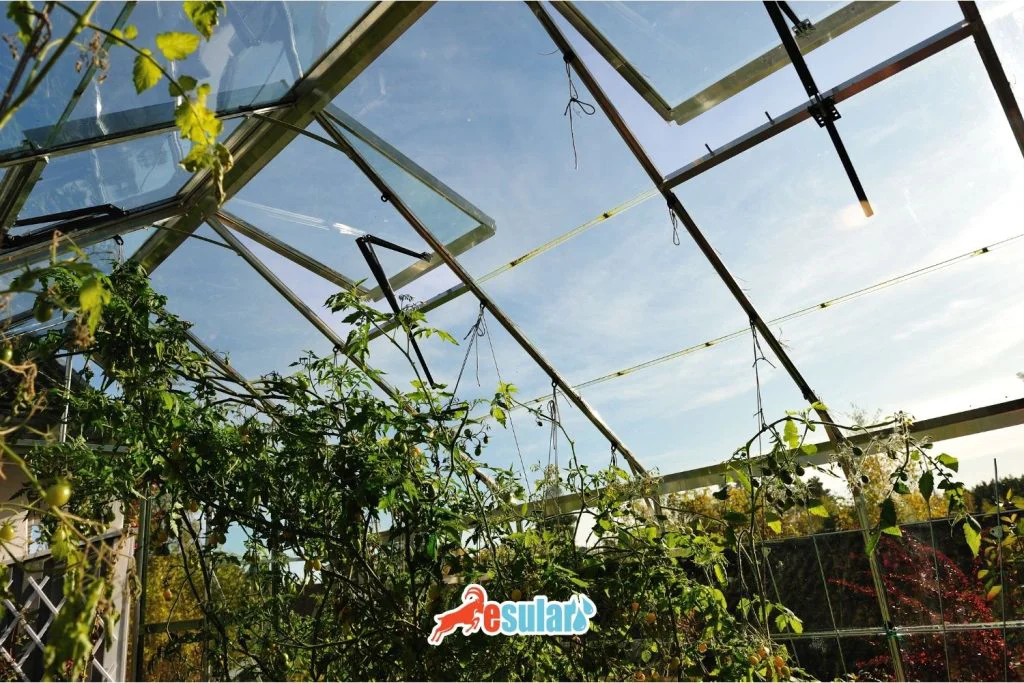
Climate control systems play a critical role in maintaining the productivity of greenhouses and plant health. These systems ensure that plants remain in optimal growth conditions by controlling humidity levels. Integrated systems continuously monitor environmental conditions with temperature and humidity sensors. When sensors detect that temperature or humidity has risen to unusual levels, they automatically activate the ventilation system. This is achieved by opening the windows and vents in the greenhouse, allowing excess humidity to be expelled. Additionally, ventilation systems play an important role in temperature control. For example, when the temperature rises too high, the ventilation fans inside the greenhouse activate and provide a flow of cool air, preventing the plants from overheating. This integrated system creates a stable microclimate necessary for the healthy growth of plants. Greenhouse owners can optimize plant health while saving energy thanks to these smart systems. For more information and solutions suitable for your needs, you can contact us.


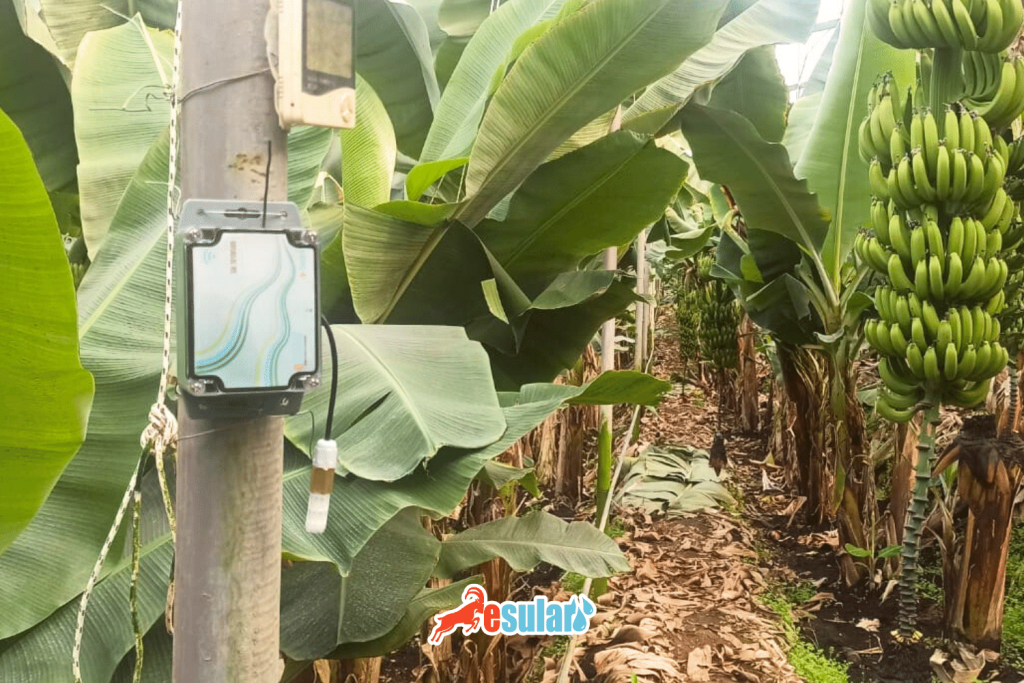
What is a Humidity and Temperature Sensor?
A wireless battery-powered humidity and temperature sensor is a device designed to determine the humidity level and temperature of the environment. It is generally used in plant cultivation environments such as greenhouses. This sensor operates with a 3.6V lithium-ion battery and does not require an external power source, which makes installation and use easy. The sensor has a single input and measures the humidity and temperature levels of the environment at certain intervals through this input. The measured data is transferred to a server using wireless communication technology. In this way, users can monitor the instant status of the environment by providing remote access and intervene when necessary. The data provided by the sensor facilitates the management of the area where it is applied. For example, it becomes possible to monitor humidity and temperature levels to provide optimum growth conditions for plants and take measures such as irrigation or ventilation when necessary. This makes the plant cultivation process more efficient and increases product quality.

How Should Greenhouse Humidity and Temperature Values Be?
Optimum Temperature and Humidity Conditions in Greenhouses
1. Greenhouse Temperature Conditions:
Daytime and nighttime temperature ranges according to plant species are as follows:
| Plant Type | Germination Period (°C) | Growth Period (°C) | Harvest Period (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cucumber | 17-18 | 17-18 | 18-20 |
| Melon | 17-18 | 17-18 | 18-20 |
| Watermelon | 17-18 | 17-18 | 18-20 |
| Tomato | 10-12 | 10-13 | 15-17 |
| Pepper | 10-12 | 10-13 | 15-17 |
| Bean | 10-12 | 10-13 | 15-17 |
| Lettuce | 8-9 | 8-12 | – |
- There should be a 5-8°C difference between daytime and nighttime temperatures inside the greenhouse.
- On cold days, the temperature should not fall below 15°C, and on sunny days, it should not exceed 30°C.
- Temperature inside the greenhouse is controlled with heaters and solar radiation.
2. Root Zone Temperature:
- Root zone temperature is critical for plant growth, shoot formation, and flowering.
- Soil temperature affects the development of the plant root system. When staying outside optimum values, yield and quality may decrease.
3. In-Greenhouse Relative Humidity Conditions:
Recommended relative humidity values according to plant species:
| Plant Type | Optimum Relative Humidity (%) |
|---|---|
| Cucumber | 85-95 |
| Melon | 65-75 |
| Watermelon | 65-75 |
| Tomato | 50-60 |
| Pepper | 50-60 |
| Bean | 50-60 |
| Lettuce | 70-80 |
| Celery | 70-80 |
| Spinach | 70-80 |
| Parsley | 70-80 |
| Cabbage | 65-75 |
- Optimum relative humidity values may vary depending on the plant species grown, greenhouse temperature, and light intensity.
- High relative humidity can create a suitable environment for pathogenic organisms; low relative humidity can lead to water loss and wilting in plants.
4. Soil Moisture Conditions:
- It is important to have water at a level above the wilting point, close to field capacity.
- Soil moisture is maintained and evaporation is reduced through mulching (plastic covering) on the soil and regular hoeing.
These conditions are important to support the healthy development of plants and to obtain optimum yield. In-greenhouse climate management should be organized to meet the requirements of plant species.



Yorumlar