Vertical Farming Systems
We will discuss vertical farming systems in detail in the following article; Vertical farming systems are classified according to their construction methods as follows;
Open: Exposed to sunlight and elements (Rooftop, open air farms).
Enclosed: Protected from the elements, but sunlight is still used for heating and lighting.
Closed: Does not receive natural sunlight. LED plant lighting technology is used for the plants.
Other: Does not receive natural sunlight. Plants are grown using other plant lighting technologies.
Vertical farming is divided into three within soilless agriculture according to the growing environments: 1. Aeroponic 2. Aquaponic 3. Hydroponic
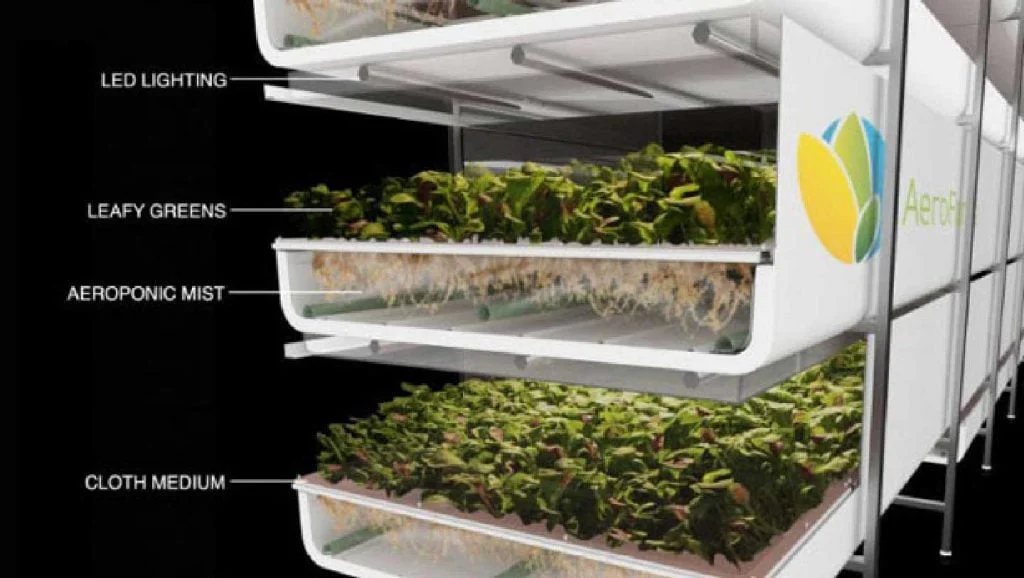
Aeroponic Systems
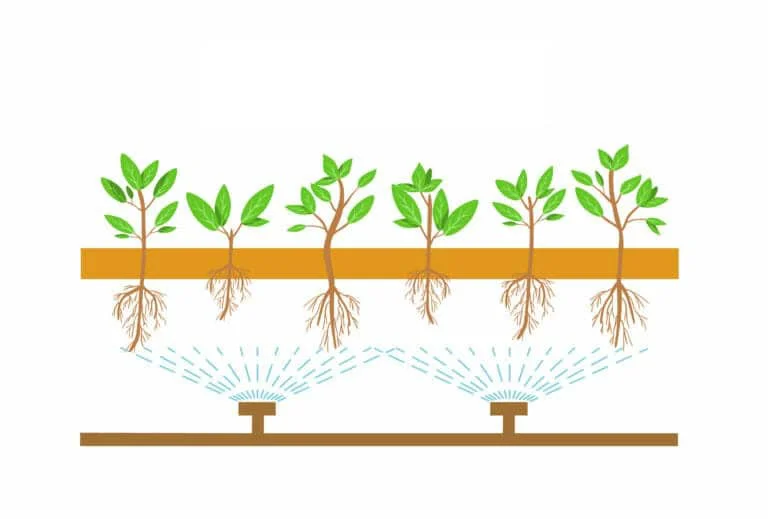
Aeroponic systems are basically air-water culture based on the principle of providing nutrient solutions to the bare root system in intermittent or continuous form. In the system, water and nutrients, which have been predetermined according to the plant species to be grown, are sprayed from the water basin to the root system through modular systems via a pump channel connected to a timer to meet the plant requirements.
The biggest advantage of the system is that it provides economy in water and fertilizer use. Since low-quality waters are also easily used in this system, it can be successfully used in regions where water quality is low.
The disadvantage of the aeroponic system is the necessity of treating these basins with a hydrogen peroxide solution to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi because the chamber where the roots hang is constantly moist.

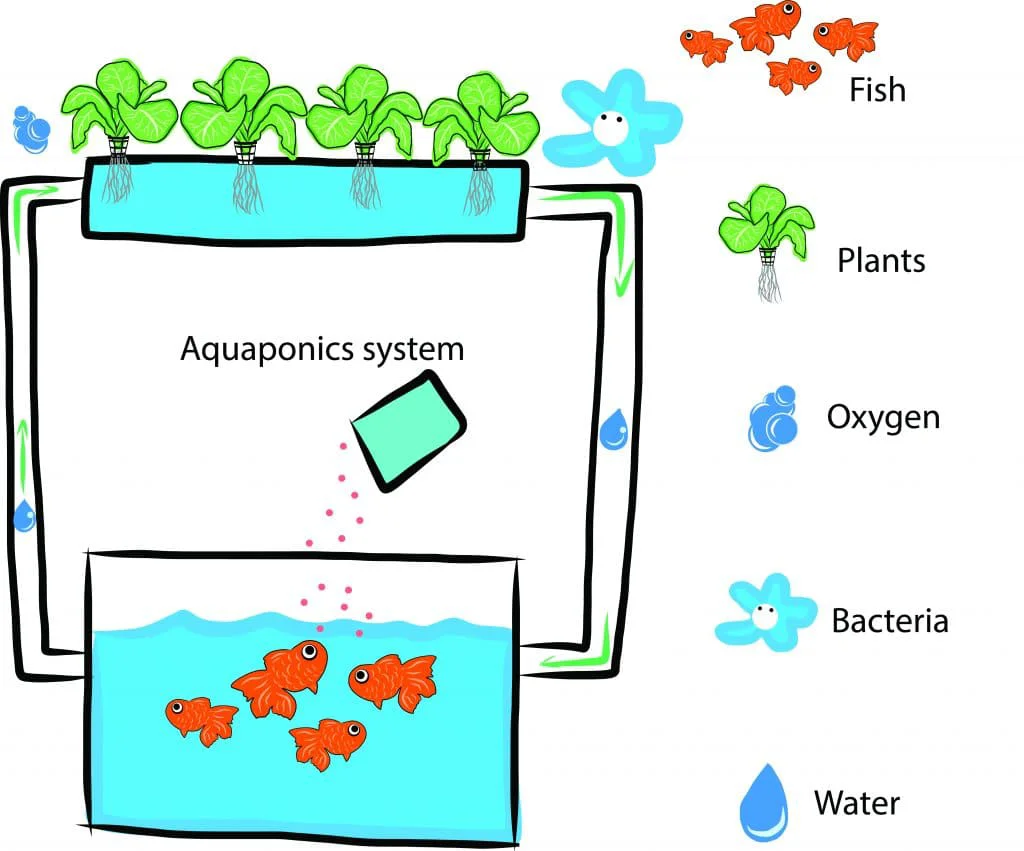
Aquaponic Systems
Aquaponics is one of the sustainable food production system alternatives with the combination of traditional Aquaculture (production of aquatic creatures such as fish, crayfish, shrimp) and the Hydroponic system. Aquaponics is an application based on the use of water used in aquaculture in hydroponic systems. The main purpose in this system is to reduce or completely eliminate the pollution load of the water used in aquaculture. The water used in fish farming is quite rich in nutritional elements. By providing this water to hydroponic systems, plants benefit from the nutritional elements. The water is filtered by the plants, and the plants serve as the treatment unit of the cultivation unit. The pollution load of the water treated by the plants is reduced. The system is in the form of bringing the water used in aquaculture to the tanks where the plants are grown via pipes or opening holes in the pipes wide enough for the plants to be placed there.
Hydroponic Systems
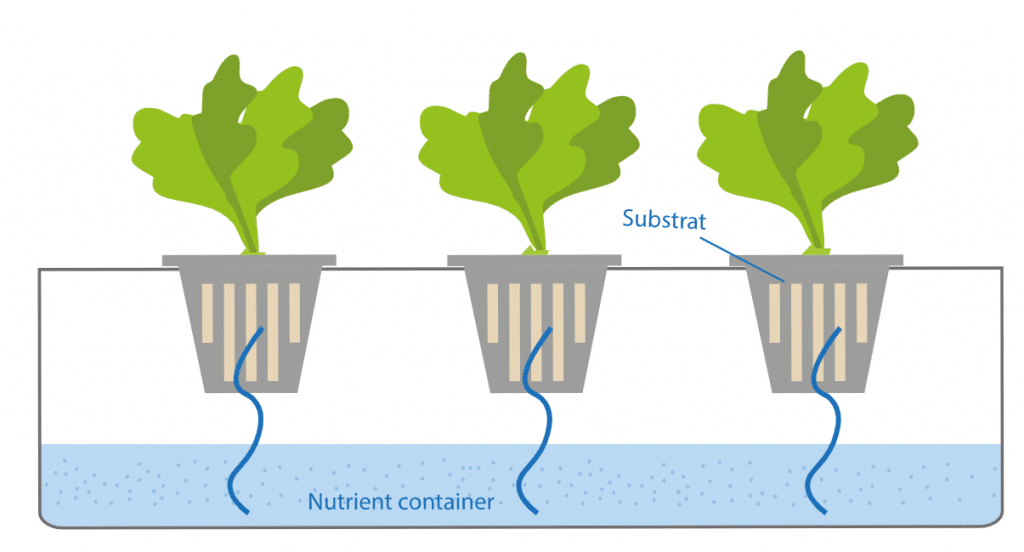
Hydroponic systems appear as the first technique used in soilless agriculture. Hydroponic, in its literal meaning, refers to growing plants in a nutrient solution without support. Along with this, growing plants in a solid medium using a nutrient solution is also included within the hydroponic system.
Hydroponic systems are divided into two as liquid or aggregate systems. While there is no solid medium supporting the plant roots in liquid systems, there is solid medium support in aggregate systems. Apart from this classification, hydroponic systems can also be called open and closed systems. In the open system, the nutrient solution is given to the plant roots once and is not reused. In the closed system, the excess solution is recollected and circulated.
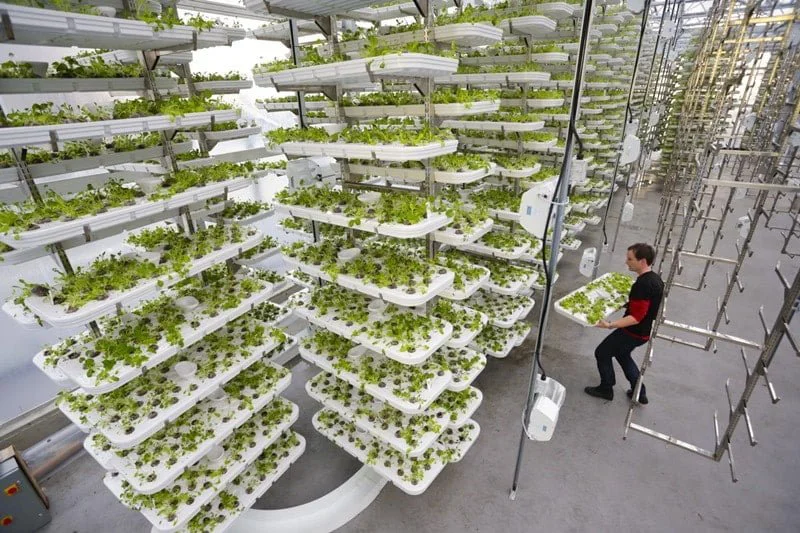
How Is Vertical Farming Done?
Regarding how vertical farming is done, many vertical fields are designed as indoor environments similar to greenhouses or are positioned by stacking on top of each other or inclined for the purpose of receiving better light. In cases where space saving is a priority, the low load provided by soilless production and water savings of up to 70 percent are preferred. In most vertical fields, the possibility of weight posing a problem is eliminated by using either the soilless method or the aeroponic method.
In vertical farming, natural daylight and artificial light are generally used together. Artificial lighting usually consists of systems that use LED technology and operate using renewable energy thanks to solar energy or wind energy.
What is Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming is an innovative method where fruits and vegetables are produced in a different way from traditional agricultural areas. This method is generally designed for use in challenging conditions where fertile soil is limited or unavailable. Vertical farming can also be applied with soilless growing methods such as aeroponic or hydroponic systems, where soil use is minimal or non-existent.
Successfully used in various environments from mountainous regions to deserts and dense urban areas, this method is carried out using skyscraper-like structures or focused farming techniques. These designs make it possible to stack products vertically in order to obtain maximum yield in a limited area.
Advantages of vertical farming include factors such as water savings, reduced dependence on seasons, optimization of agricultural areas, and increasing food production in cities. This method offers a sustainable and efficient farming practice by overcoming the soil limitations that traditional agriculture struggles with.

Where is Vertical Farming Done?
Vertical farming is an agricultural method usually applied in indoor environments. Vertical fields can be designed as indoor structures similar to greenhouses, and products are grown either by stacking them on top of each other or by positioning them at an angle to receive better light. This method is preferred especially when space saving is important, and water savings of up to 70 percent can be achieved using soilless production methods.
Today, methods and innovations used in the field of vertical farming focus on making agriculture more sustainable, productive, and effective. Here are some ideas that could shape the future of vertical farming:
Soilless Growing Methods:
- Vertical farming is generally applied with soilless growing methods. Hydroponic and aeroponic systems allow plants to receive nutrients in a water environment.
Designs Reducing Weight Problems:
- Weight problems can occur in high-rise buildings or vertical farming systems. Innovative designs may include lightweight and durable materials to reduce this problem.
Light and Energy Efficiency:
- Adequate light intake is critical for the success of vertical farming. Energy costs can be reduced and plant growth can be optimized by using LED and other energy-efficient lighting systems.
Smart Farming and Sensor Technologies:
- Sensors used in the field of vertical farming can monitor soil moisture, plant health, and other important factors. This data can be analyzed through smart farming applications to optimize irrigation and other agricultural processes.
Robotic Farming Systems:
- Vertical farming can be integrated with robots and automated systems. These systems can automate plant care, harvesting, and other processes, reducing human intervention.
Plant Genetic Engineering:
- Plant genetic engineering can be used to increase the efficiency of vertical farming and produce plants suitable for special needs.
These innovations can carry the future of vertical farming in a more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally friendly direction.
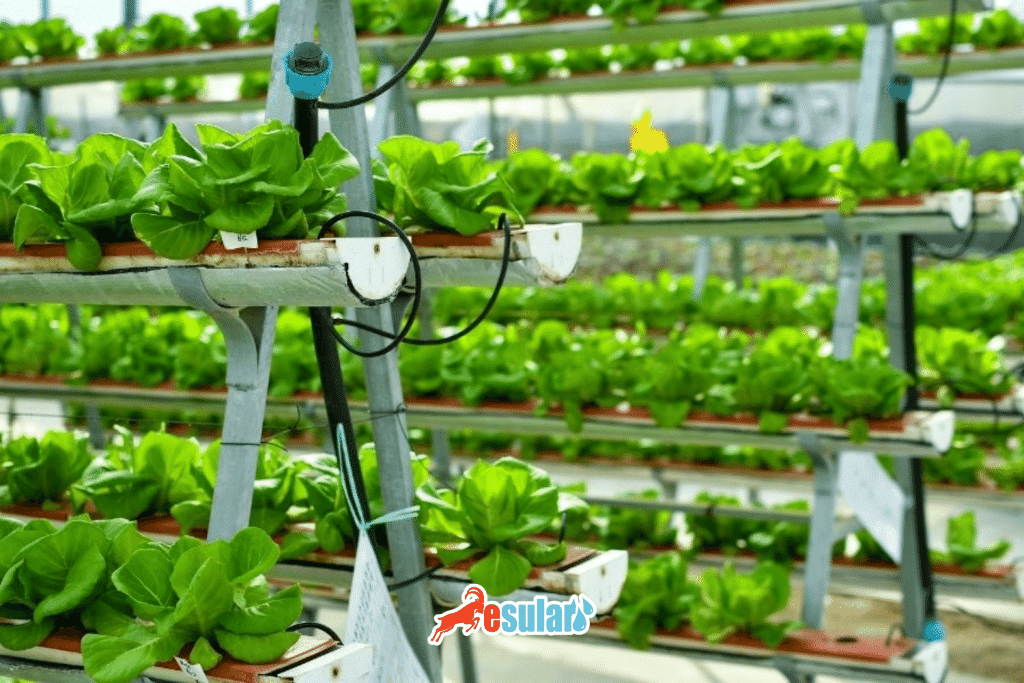

Light Usage in Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is an agricultural method where plants are grown vertically on top of each other or within high structures. Light is one of the most critical elements of vertical farming and plays a vital role for plants to grow healthily, photosynthesize, and yield products efficiently. Here are some factors indicating the importance of light in vertical farming:
Photosynthesis and Plant Growth:
- Light is a fundamental requirement for plants to photosynthesize. Photosynthesis is a basic biochemical process that allows plants to produce glucose by combining water and carbon dioxide using sunlight. This process is critical for plant growth, energy storage, and product yield.
Light Spectrum:
- Plants need specific light spectrums. Blue and red lights are generally known as the spectrums that most encourage photosynthesis. Special lighting systems used in vertical farming systems are designed to provide the specific light wavelengths that plants need.
Light Duration and Photoperiod:
- Plants need a specific light duration (photoperiod). Some plants are short-day plants, meaning their flowering and fruiting processes occur on short days, while some are long-day plants. In vertical farming systems, light duration can be controlled depending on the plant species and growth stage.
Energy Efficiency:
- Artificial lighting used in vertical farming systems is important in terms of energy efficiency. LED lights are frequently preferred in vertical farming applications due to their low energy consumption, long life, and the ability to control specific wavelengths.
Plant Morphology and Arrangement:
- One of the advantages of vertical farming is the ability to create controllable environments where plants are arranged regularly and light is distributed more homogeneously. This arrangement can shape plant morphology and increase the effective use of light.
Light is a fundamental parameter of vertical farming, and the lighting technologies used in this system are constantly being developed to provide the special light conditions that plants need.
Can Vertical Farming Be Done?
Vertical farming practices are being carried out and used in various places worldwide. Vertical farming is an agricultural method involving growing plants in a vertical arrangement, stacked on top of each other or in high structures. This method offers an alternative to traditional farming methods by providing advantages such as limited land use, water savings, seasonal independence, and high efficiency.
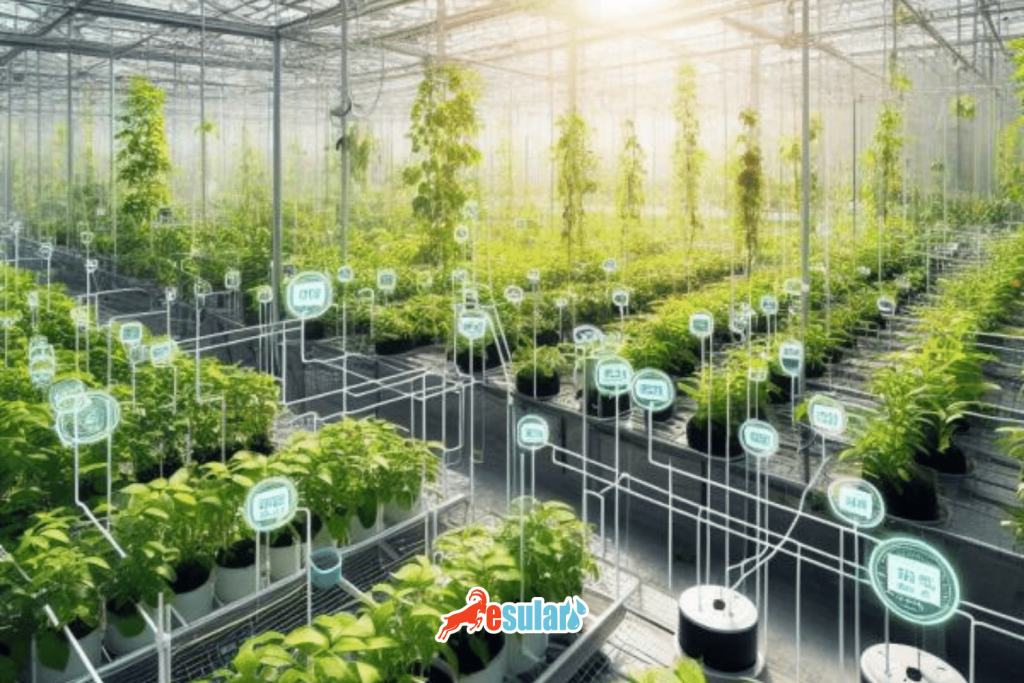

Advantages of Vertical Farming
The biggest advantage of vertical farming is water savings of up to 75% and the absence of pesticides for weeds and plant diseases since it is done in indoor environments. Apart from this, depending on the technique applied, it is possible to produce non-stop for 365 days.

Vertical farming is a modern agricultural method where plants are grown vertically on top of each other or in high structures. This method has many advantages, especially related to factors such as limited land use, water savings, and seasonal independence. Here are the advantages of vertical farming:
Land Saving:
- Vertical farming uses much less horizontal space compared to traditional farming methods. Since plants are grown by stacking on top of each other or side by side within vertical structures, it provides the opportunity to grow more products on limited land.
Water Saving:
- Vertical farming systems are generally integrated with soilless or hydroponic systems. These systems optimize water use and provide significant water savings compared to traditional farming methods.
Seasonal Independence:
- Vertical farming can reduce dependence on seasons. Vertical farming carried out under controlled conditions in indoor environments is less exposed to the external effects of weather conditions and enables continuous production throughout the year.
Plant Health and Control:
- Vertical farming systems provide an advantage in keeping plant health under control. Sensors and automation technologies used in these systems optimize factors such as water, nutrients, and light, ensuring plants grow in the best conditions.
High Efficiency:
- Vertical farming makes it possible to obtain higher yields per unit by providing a denser plant population. This is particularly advantageous in cases where agricultural area is limited.
Reduction in Nitrogen and Pesticide Use:
- Vertical farming provides a more controlled environment than traditional farming methods. This allows for more effective and localized use of chemical substances such as nitrogen and pesticides, reducing environmental impact.
Urban Farming:
- Vertical farming can be carried out in compatibility with limited land use in cities. This supports local food production and sustainable agriculture within the city.
Constant Production Year-Round:
- Vertical farming done in indoor environments does not depend on seasons and supports constant production throughout the year.
These advantages of vertical farming can contribute to making agriculture more sustainable and efficient in the future.

Yorumlar