Water Management
Water management is the process of planned and effective use, distribution, protection, and sustainable management of water resources. Sustainable water management is an approach that aims for the long-term use and management of water resources. This approach aims to transfer existing water resources to future generations in a sufficient and healthy manner.
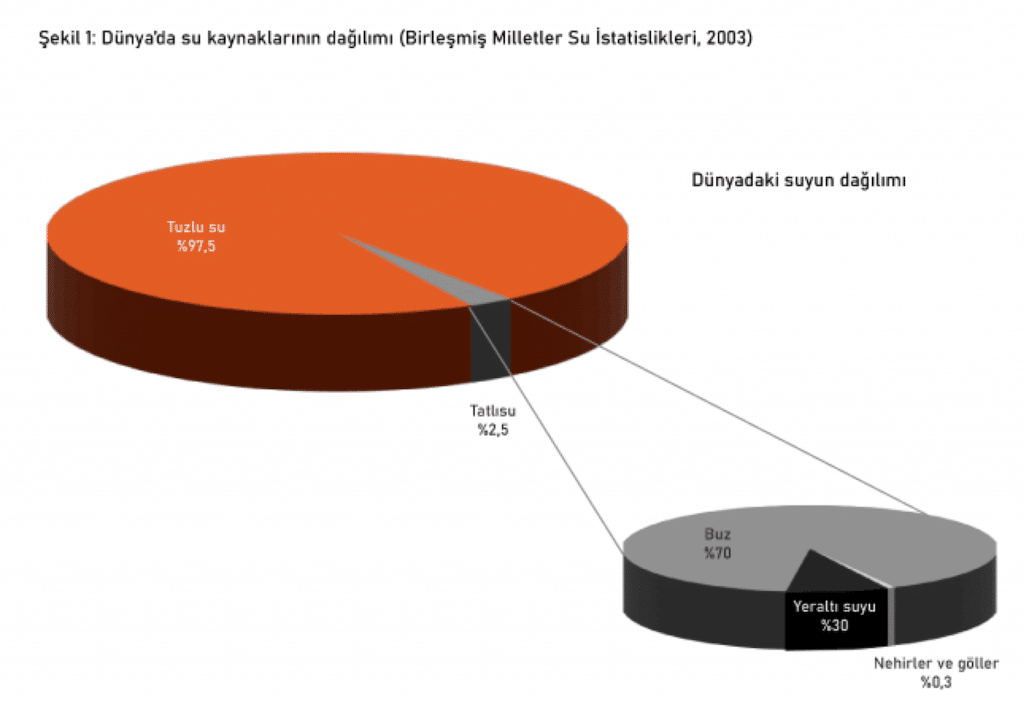
Although 75% of the Earth's surface is covered with water, the amount of freshwater suitable for human use is quite limited. The total freshwater ratio on Earth is 2.5%, and a large part of this amount is trapped in poles, glaciers, and underground reserves. The ratio of freshwater resources that constitute the part suitable for ecosystem and human use corresponds to only 0.3% (UN Water Statistics, 2003). In light of these data, we can say that 'water scarcity is a subject as old as human history'.
Turkey, contrary to general public perception, is a country on the edge of water scarcity. The annual precipitation amount remains below the world average. The use of our country's water resources showed a great increase between 1990-2010, and total water consumption increased by 40.5%. It is estimated that the need for water may triple today's consumption within the next 25 years. Water scarcity will be one of the most important problems in the future. In the past 50 years, although the amount of water resources has remained the same, water withdrawal has tripled (WWAP, 2012). In many regions, groundwater withdrawals are above replenishment or sustainable levels. In 2030, it is estimated that food, water, and energy needs will increase by approximately 50%. Climate change will make the current status of these resources even more critical. The future of water has never been so ambiguous. It is vital that studies for climate change focus on water.
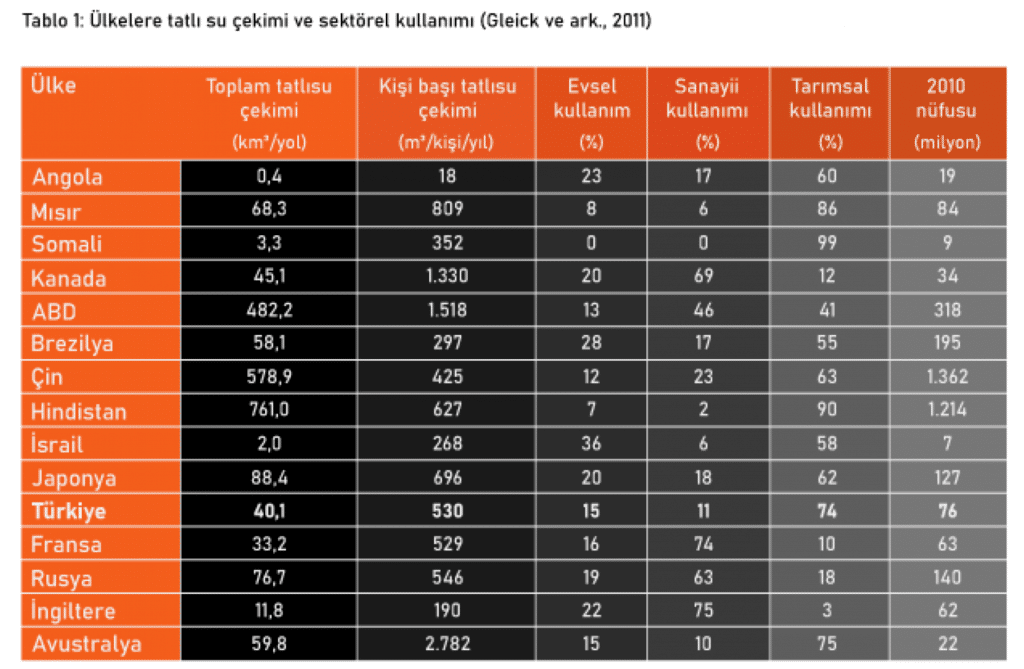
Approximately 70% of the world's water resources are used for agricultural purposes. This is followed by industrial and domestic use with 19% and 11% (FAO Aquastat, 2013). In our country, 77% is used for agricultural purposes. Table 1 shows water withdrawal amounts and sectoral usage amounts in various countries.
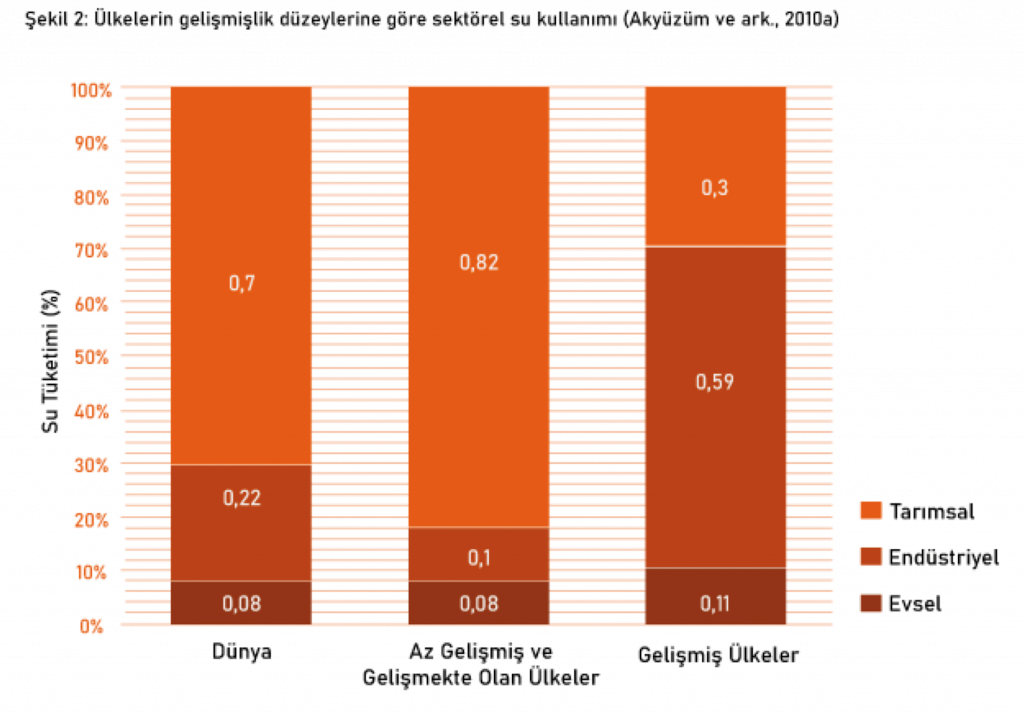
Sectoral water use is an indicator reflecting the development levels of countries. While the average agricultural water consumption in underdeveloped and developing countries is generally around 82%, this rate drops to 30% in developed countries (WWAP, 2003). In countries with high income levels, agricultural water use generally gives way to the industrial sector (Aküzüm et al., 2010). According to 2003 data, water use rates in different sectors worldwide are given in the Figure according to the development levels of the countries.
According to the OECD report, in the coming years, the agricultural sector will face a major problem such as meeting the increasing food demand. According to estimates, global food consumption will increase by 50% in 2030 and by 100% in 2050 compared to the present (OECD, 2012a). Due to factors such as urbanization, industrialization, and climate change, agriculture will need to be carried out with less water. Therefore, developing agricultural water planning is of great importance. According to the report prepared by the United Nations, it is estimated that agricultural production in developing countries will increase by 67% between 2000-2030 (WWAP, 2006). It is predicted that this increase cannot be met with the current water potential and can be met by keeping the increase in agricultural water need at 14% through productivity increases in agriculture. In this case, the agricultural sector will have to produce more agricultural products using less water (WWAP, 2006). There is a complex relationship between agriculture and climate change. Agricultural activities cause climate changes through the emission of methane and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. However, at the same time, agriculture is one of the sectors that will be most affected by the effects of climate change.
Drought emerges as a problem that threatens agricultural sustainability today. Our country has been struggling with a serious drought for a long time, and this situation negatively affects agricultural production. There are also concerns that the drought problem may worsen in the future. Therefore, efficient management of water resources and sustainable water use are of great importance. Sustainable water management offers an effective solution to reduce the effects of drought and ensure agricultural sustainability. This approach includes encouraging the efficient use of water resources, ensuring the adoption of modern irrigation techniques, expanding water-saving practices, and providing support to farmers. Sustainable water management plays a critical role in issues such as the protection of water resources, sustainability of agriculture, and the fight against climate change. To achieve these goals, strategies such as education, awareness-raising, policy development, and stakeholder cooperation should also be used effectively.
In Turkey, important steps have been taken regarding the management of water in recent years. In 2021, the first 'Water Council' of our Republic's history was held. As stated in the closing meeting of the Water Council, '"Water Will Be the Most Strategic Asset of the Next 100 Years"'. On October 21, 2021, the 28-article Water Council Final Declaration was published. Looking at the prominent articles;
- Preparation of the Water Efficiency Strategy Document and Basin-Based Water Efficiency Action Plans.
- Reduction of the water loss rate in drinking water systems, which is at the 35% level in municipalities, to below the 25% level. Starting studies related to full cost-based water and wastewater pricing as of 2023 in order to provide sustainable water services,
- Within the scope of the European Green Deal, ensuring the reuse of wastewater, primarily for agricultural irrigation, by bringing it to appropriate quality,
- For the purpose of protecting, improving, and ensuring the sustainable management of our water resources, completing and implementing basin-scale management plans for 25 basins,
- Enacting a Water Law that will eliminate the fragmented structure in water management, remove gaps in the current legal structure, and comply with the legislation on water quality included in the European Union environment and climate change chapter,
- Analyzing the effects of climate change on water resources as part of climate change adaptation activities, which gained importance with the approval of the Paris Agreement in the GNAT,
- Expanding the irrigation of economically irrigable lands with modern irrigation methods,
- Developing new financing models including the private sector in irrigation projects.
- Determining the product pattern according to the basin water potential and basing it on the agriculture-according-to-water approach,
- Achieving water-saving goals by providing remote control and automation of irrigation facilities with digital technologies and increasing measures aimed at reducing energy costs in irrigation,
- Carrying out education and awareness-raising activities to develop water, meteorology, and climate change literacy for all segments of society,
- Ensuring the support and development of R&D studies regarding water management.
Inter-institutional coordination must be ensured for the protection and sustainable management of our water resources, which are a right to life. Water management is not the business of certain groups, but a matter for all humanity and life. Technology has a driving force in providing the predicted yield increase and using resources efficiently. The effectiveness of the scientific process in the sustainable use and management of soil and water resources should be increased, and a culture of using advanced technology should be developed.



Yorumlar